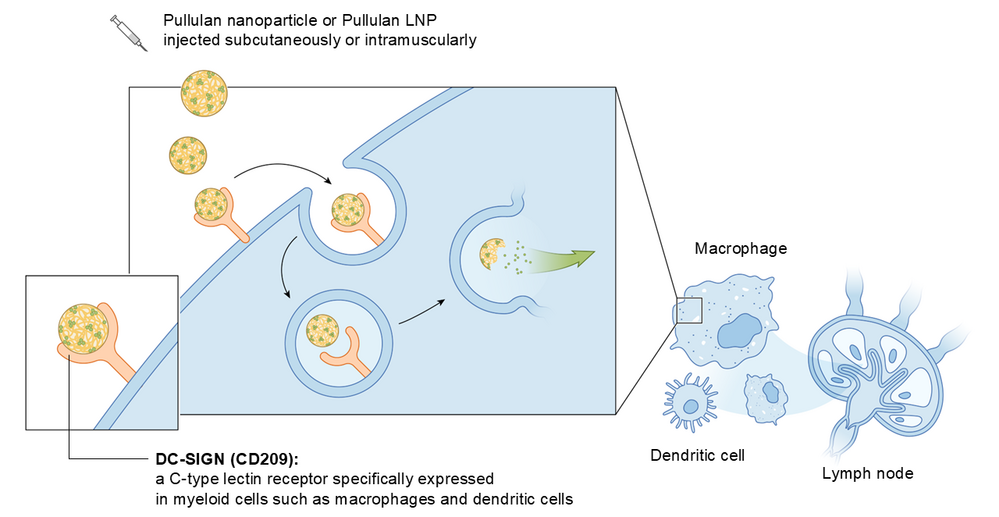
Myeloid Specific Cell Receptor DC-SIGN
Targeting of pullulan nanoparticle (PNP) and pullulan-coated lipid nanoparticle (P-LNP) to myeloid cells is achieved by specific binding of pullulan polysaccharide contained in these nanoparticles to a C-type lectin receptor DC-SIGN (also known as CD209) (PAT pending). DC-SIGN is present on the surface of macrophages, dendritic cells, Kupffer cells (liver), Langerhans cells (skin), Hoffbauer cells (placenta), adipose tissue macrophages, and microglia. A physiological role of DC-SIGN is sensing of polysaccharides on pathogens and promotion of their internalization into these cells. DC-SIGN also mediates the contact between antigen-presenting dendritic cells and macrophages to T cells.
In many types of solid tumors, DC-SIGN is predominantly expressed in anti-inflammatory M2-like tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) which promote immune suppression within the tumor microenvironment. Expression of DC-SIGN or frequency of M2-like TAMs are reported to be associated with tumor progression, poor prognosis and treatment resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors.